Notes from AWS tech essentials and cloud practitioner essentials.
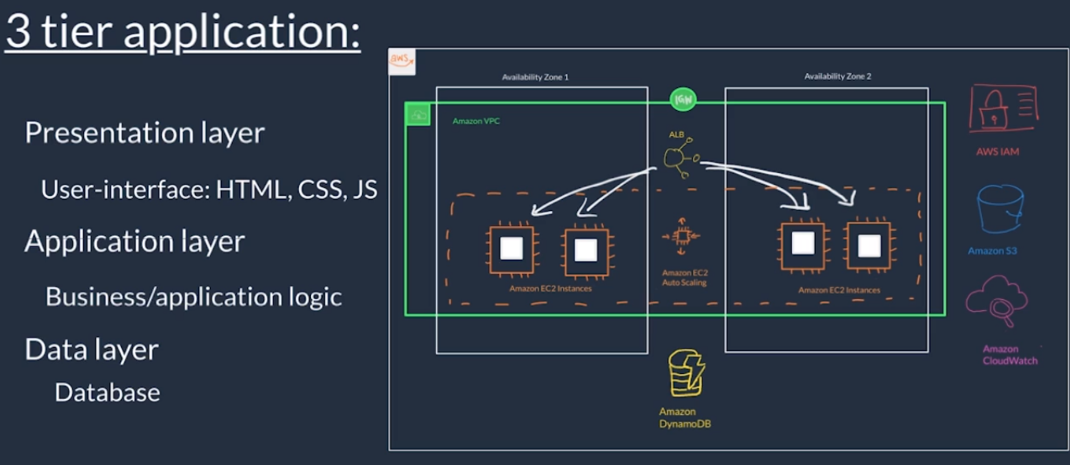
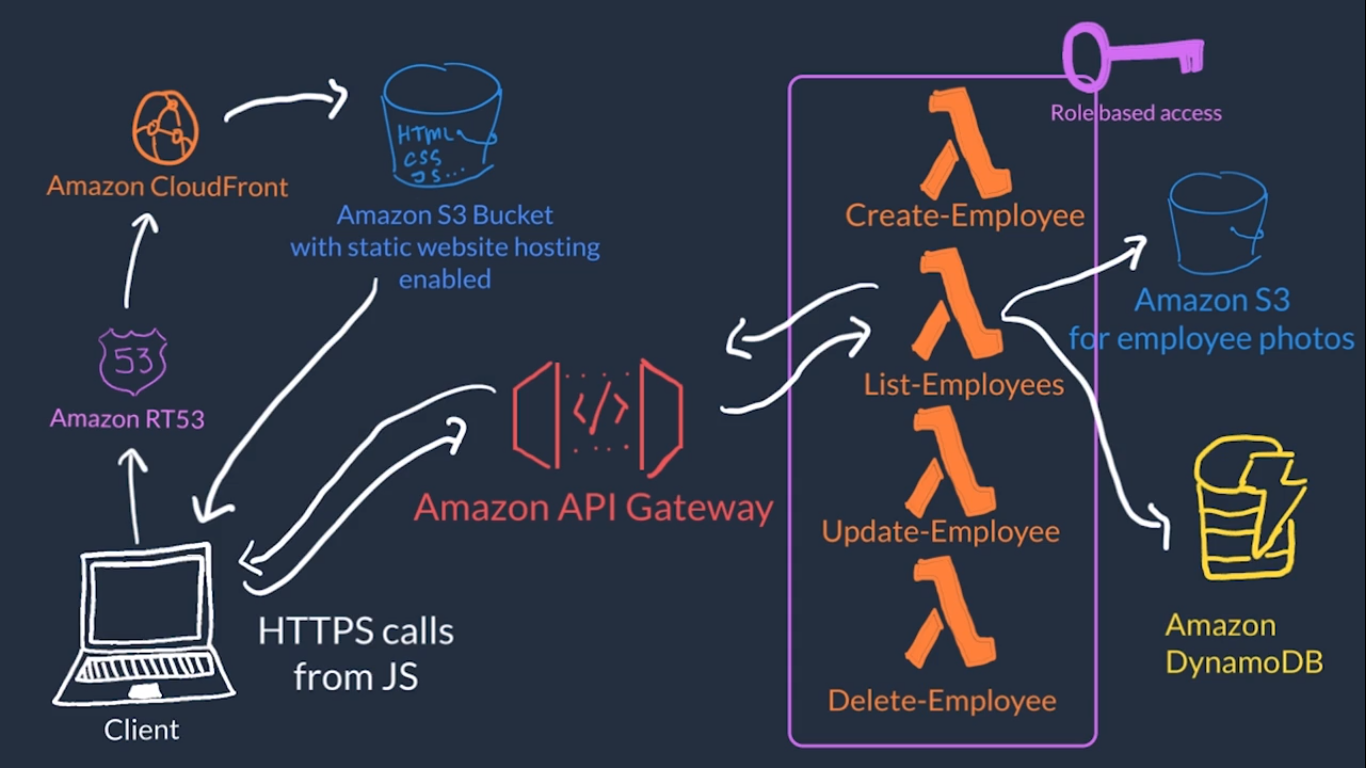
- Overview of Amazon Web Services
- AWS Fundamentals: Core Concepts
- The AWS Well-Architected Framework helps you understand how to design and operate reliable, secure, efficient, and cost-effective systems in the AWS Cloud.
- The Performance Efficiency pillar focuses on using computing resources efficiently to meet system requirements, and to maintain that efficiency as demand changes and technologies evolve.
- The Operational Excellence pillar includes the ability to run workloads effectively, gain insights into their operations, and continuously improve supporting processes to deliver business value.
- The Security pillar focuses on protecting data, systems, and assets. It also focuses on using cloud technologies to improve the security of your workloads.
- The Reliability pillar focuses on the ability of a workload to consistently and correctly perform its intended functions.
- Global infrastructure
- region (bound to compliance, latency, service availability, price)
- AZ
- data centers
- Shared responsibility model
- Security Best Practices in IAM
- Permissions are defined in a form of policies which can be attached to a user, group or role.
- An IAM role is an identity that you can assume to gain temporary access to permissions. Before an IAM user, application, or service can assume an IAM role, they must be granted permissions to switch to the role. When someone assumes an IAM role, they abandon all previous permissions that they had under a previous role and assume the permissions of the new role. IAM roles are ideal for situations in which access to services or resources needs to be granted temporarily, instead of long-term.
- In AWS Organizations, you can apply service control policies (SCPs) to the organization root, an individual member account, or an OU. An SCP affects all IAM users, groups, and roles within an account, including the AWS account root user.
- AWS Artifact is a service that provides on-demand access to AWS security and compliance reports and select online agreements. AWS Artifact consists of two main sections: AWS Artifact Agreements and AWS Artifact Reports.
- AWS Shield is a service that protects applications against DDoS attacks. AWS Shield provides two levels of protection: Standard and Advanced.
- AWS Key Management Service (AWS KMS) enables you to perform encryption operations through the use of cryptographic keys. A cryptographic key is a random string of digits used for locking (encrypting) and unlocking (decrypting) data.
- AWS WAF is a web application firewall that lets you monitor network requests that come into your web applications. It does this by using a web access control list (ACL) to protect your AWS resources.
- Amazon Inspector helps to improve the security and compliance of applications by running automated security assessments. It checks applications for security vulnerabilities and deviations from security best practices, such as open access to Amazon EC2 instances and installations of vulnerable software versions.
- Amazon GuardDuty is a service that provides intelligent threat detection for your AWS infrastructure and resources. It identifies threats by continuously monitoring the network activity and account behavior within your AWS environment.
- Whitepaper: Amazon Web Services - Overview of Security Processes
- Compute options
- VMs
- container services
- serverless (abstrated services)
- Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS) is a highly scalable, high-performance container management system that enables you to run and scale containerized applications on AWS. Amazon ECS supports Docker containers.
- Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (Amazon EKS) is a fully managed service that you can use to run Kubernetes on AWS.
- AWS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers. It works with both Amazon ECS and Amazon EKS. When using AWS Fargate, you do not need to provision or manage servers. AWS Fargate manages your server infrastructure for you.
- AMI IDs are different in each region.
- AWS Serverless Resources
- Deep Dive Serverless
- Best practices for organizing larger serverless applications
- 10 Things Serverless Architects Should Know
- AWS Alien Attack! A Serverless Adventure
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk. You upload your application, and Elastic Beanstalk automatically handles the deployment details of capacity provisioning, load balancing, auto-scaling, and application health monitoring.
- When working with networks in the AWS Cloud, you choose your network size by using CIDR notation. In AWS, the smallest IP range you can have is /28, which provides 16 IP addresses. The largest IP range you can have is a /16, which provides 65,536 IP addresses.
- VPC
- Region
- IP range
- Subnet (bound to an AZ)
- VPC
- AZ
- IP range
- VPC with Public and Private Subnets (NAT)
- Route tables for your VPC
- The default network ACL allows all traffic in and out of the subnet. To allow data to flow freely to the subnet, but you can modify it by adding your own rules. For custom network ACLs, all inbound and outbound traffic is denied until you add rules to specify which traffic to allow. Network ACLs perform stateless packet filtering. They remember nothing and check packets that cross the subnet border each way: inbound and outbound.
- The next layer of security is for your EC2 Instances. Here, you can create a firewall called a security group. The default configuration of a security group blocks all inbound traffic and allows all outbound traffic. Security groups perform stateful packet filtering. They remember previous decisions made for incoming packets. Source can be defined as IP address or security group.
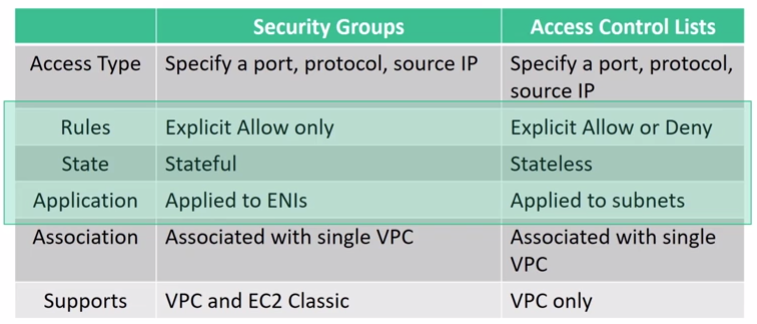
- A virtual private gateway enables you to create a VPN connection between your VPC and a private network, such as your company’s data center. Although this connection is private and encrypted, it travels through the public internet, not through a dedicated connection.
- I host a website on an EC2 instance. How do I allow my users to connect on HTTP (80) or HTTPS (443)?
- AWS storage services are grouped into three categories – block storage, file storage, and object storage.
- File storage is ideal when you require centralized access to files that need to be easily shared and managed by multiple host computers. Typically, this storage is mounted onto multiple hosts, and requires file locking and integration with existing file system communication protocols. File storage systems are often supported with a network attached storage (NAS) server. Amazon EFS and Amazon FSx can be mounted onto multiple EC2 instances.
- EFS can be mounted to a single VPC at one time. It is regional resource and automatically scales. It can scale on demand to petabytes without disrupting applications. It uses NFS v4.1 protocol.It uses security group to control the access. Only compatible with Linux AMI.
- While file storage treats files as a singular unit, block storage splits files into fixed-size chunks of data called blocks that have their own addresses. Since each block is addressable, blocks can be retrieved efficiently. Block storage in the cloud is analogous to direct-attached storage (DAS) or a storage area network (SAN).
- Most EBS volumes can only be attached to a single EC2 instance at a time. Size up to 16 TB. Need to be the same AZ to attach EC2 instances. Volumes don’t scale automatically.
- Objects, much like files, are treated as a single unit of data when stored. However, unlike file storage, these objects are stored in a flat structure instead of a hierarchy. Each object is a file with a unique identifier. This identifier, along with any additional metadata, is bundled with the data and stored. Amazon S3 is not storage attached to compute.
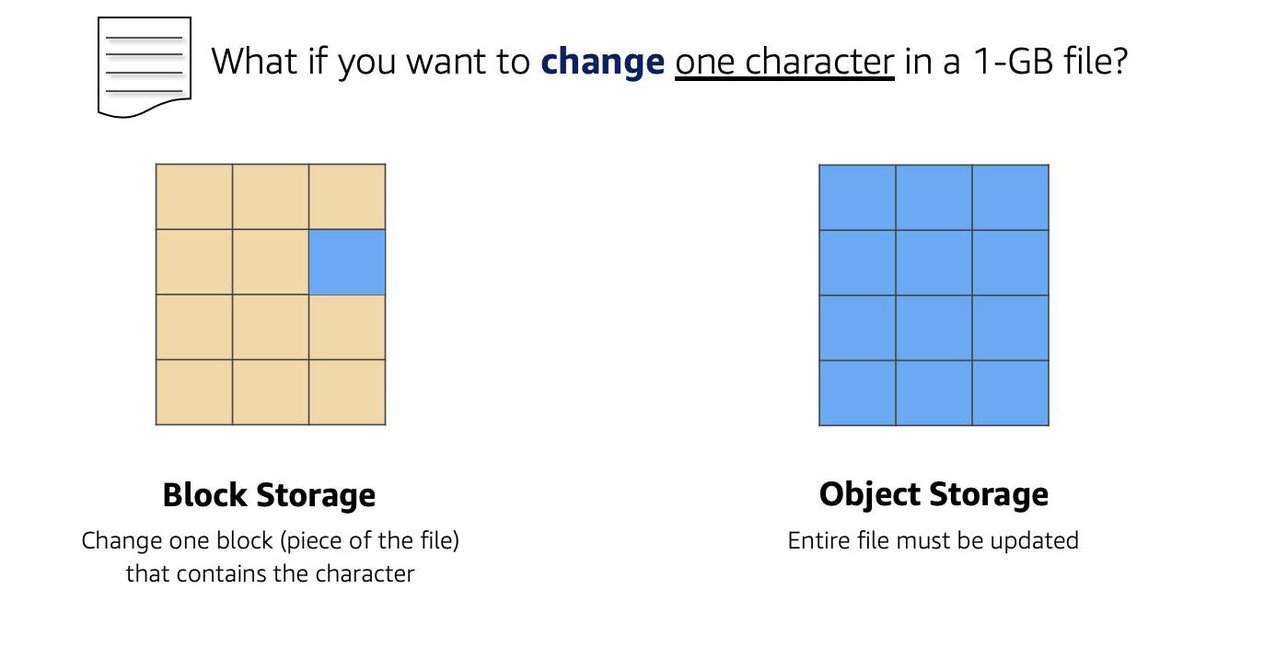
- EC2 instance store is often referred to as ephemeral block storage.
- Amazon S3 Storage Classes, write once / read many.
- S3 Standard-IA provides the same level of availability of S3 Standard, but at a lower storage price and higher retrieval price.
- In the S3 Intelligent-Tiering storage class, Amazon S3 monitors objects’ access patterns. If you haven’t accessed an object for 30 consecutive days, Amazon S3 automatically moves it to the infrequent access tier, S3 Standard-IA.
- S3 has provided strong consistency since Dec 2020.
- S3 encryption for data at rest: SSE-S3, SSE-KMS, SSE-C; for data in transit: HTTPS.
- Server-Side Encryption with Customer-Provided Keys (SSE-C) enables Amazon S3 to encrypt objects server side using an encryption key provided in the PUT request. The same key must be provided in GET requests for Amazon S3 to decrypt the object. Customers also have the option to encrypt data client side before uploading it to Amazon S3 and decrypting it after downloading it.
- In DynamoDB, tables, items, and attributes are the core components that you work with. A table is a collection of items, and each item is a collection of attributes. DynamoDB uses primary keys to uniquely identify each item in a table and secondary indexes to provide more querying flexibility.
- Databases on AWS
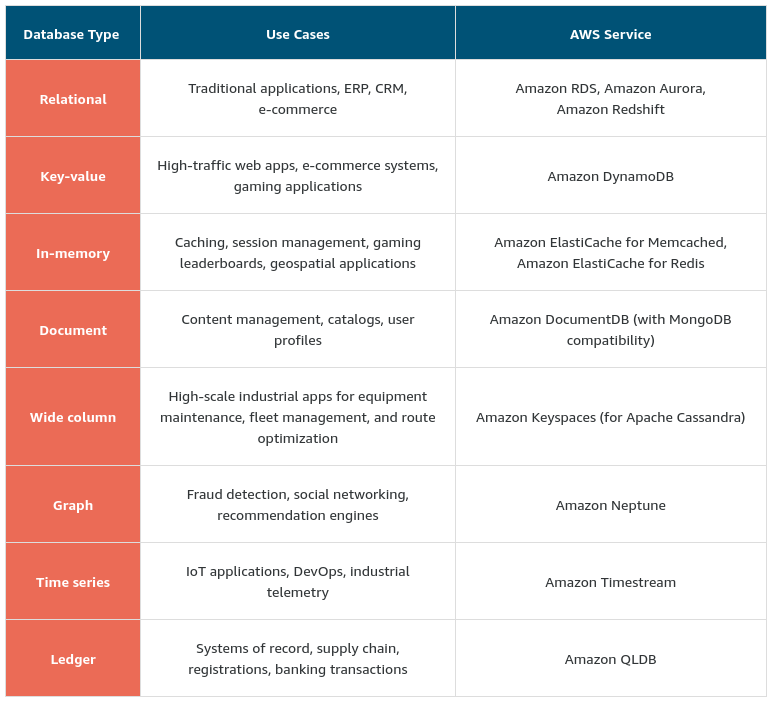
- Amazon ElastiCache is a service that adds caching layers on top of your databases to help improve the read times of common requests.
- Monitoring benefits
- Respond to operational issues proactively before your end users are aware of them.
- Improve the performance and reliability of your resources.
- Recognize security threats and events.
- Make data-driven decisions for your business.
- Create more cost-effective solutions.
- You can use CloudWatch to:
- Detect anomalous behavior in your environments
- Set alarms to alert you when something is not right
- Visualize logs and metrics with the AWS Management Console
- Take automated actions like scaling
- Troubleshoot issues
- Discover insights to keep your applications healthy
- CloudWatch Logs terminology
- Log event: A log event is a record of activity recorded by the application or resource being monitored, and it has a timestamp and an event message.
- Log stream: Log events are then grouped into log streams, which are sequences of log events that all belong to the same resource being monitored.
- Log groups: Log streams are then organized into log groups. A log group is composed of log streams that all share the same retention and permissions settings.
- CloudWatch alarms
- OK: The metric is within the defined threshold. Everything appears to be operating like normal.
- ALARM: The metric is outside the defined threshold. This could be an operational issue.
- INSUFFICIENT_DATA: The alarm has just started, the metric is not available, or not enough data is available for the metric to determine the alarm state.
- AWS CloudTrail records API calls for your account. The recorded information includes the identity of the API caller, the time of the API call, the source IP address of the API caller, and more.
- AWS Trusted Advisor is a web service that inspects your AWS environment and provides real-time recommendations in accordance with AWS best practices. Trusted Advisor compares its findings to AWS best practices in five categories: cost optimization, performance, security, fault tolerance, and service limits. For the checks in each category, Trusted Advisor offers a list of recommended actions and additional resources to learn more about AWS best practices.
- Types of high availability
- Active-Passive: With an active-passive system, only one of the two instances is available at a time. One advantage of this method is that for stateful applications where data about the client’s session is stored on the server, there won’t be any issues because the customers are always sent to the server where their session is stored.
- Active-Active: A disadvantage of active-passive and where an active-active system shines is scalability. By having both servers available, the second server can take some load for the application, allowing the entire system to take more load. However, if the application is stateful, there would be an issue if the customer’s session isn’t available on both servers. Stateless applications work better for active-active systems.
- High Availability and Scalability on AWS
- AWS Reliability Pillar: AWS Well-Architected Framework
- Elastic Load Balancer Product Comparison
-
ELB with EC2 Auto Scaling: The ELB service integrates seamlessly with EC2 Auto Scaling. As soon as a new EC2 instance is added to or removed from the EC2 Auto Scaling group, ELB is notified. However, before it can send traffic to a new EC2 instance, it needs to validate that the application running on the EC2 instance is available. This validation is done by way of the ELB health checks feature. Monitoring is an important part of load balancers, because they should route traffic to only healthy EC2 instances. That’s why ELB supports two types of health checks.
- Establishing a connection to a backend EC2 instance using TCP, and marking the instance as available if the connection is successful.
- Making an HTTP or HTTPS request to a webpage that you specify, and validating that an HTTP response code is returned.
- Configure EC2 Auto Scaling components
- Launch template or configuration: What resource should be automatically scaled? Launch template is a newer version which should be used.
- EC2 Auto Scaling Group: Where should the resources be deployed?
- Scaling policies: When should the resources be added or removed?
- Within Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling, you can use two approaches: dynamic scaling and predictive scaling.
- Dynamic scaling responds to changing demand.
- Predictive scaling automatically schedules the right number of Amazon EC2 instances based on predicted demand.
- The difference between fault tolerance and high availability, is this: A fault tolerant environment has no service interruption but a significantly higher cost, while a highly available environment has a minimal service interruption.
- Auto scaling, ELB and CloudWatch work together to enable auto scaling of EC2 instances.
- RTO: recover time objective (to bring the system online); RPO: recover point objective (how much data was lost)
- At the highest level, the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework (AWS CAF) organizes guidance into six areas of focus, called Perspectives. In general, the Business, People, and Governance Perspectives focus on business capabilities, whereas the Platform, Security, and Operations Perspectives focus on technical capabilities.
- Whitepaper: An Overview of the AWS Cloud Adoption Framework
- When migrating applications to the cloud, six of the most common migration strategies that you can implement are: Rehosting, Replatforming, Refactoring/re-architecting, Repurchasing, Retaining, Retiring
- The AWS Snow Family is a collection of physical devices that help to physically transport up to exabytes of data into and out of AWS. Snowcone - 8TB, Snowball Edge Storage Optimized - 80TB, Snowball Edge Compute Optimized - 42TB, Snowmobile - 100PB.
- The six advantages of cloud computing are:
- Trade upfront expense for variable expense.
- Benefit from massive economies of scale.
- Stop guessing capacity.
- Increase speed and agility.
- Stop spending money running and maintaining data centers.
- Go global in minutes.
Image by Free-Photos from Pixabay